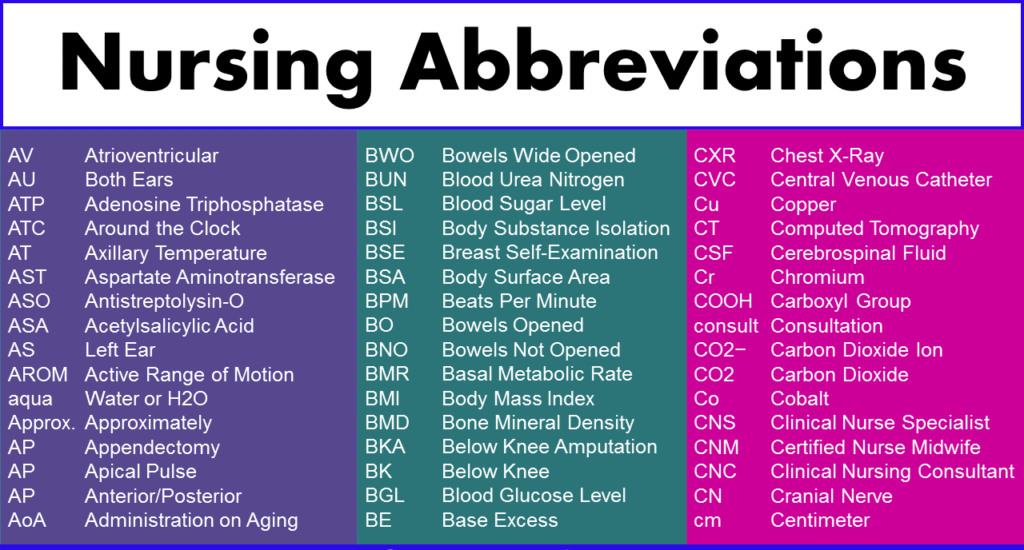
From A to Z: The Essential Short Forms Every Medical Student Should Know
Introduction: In the fast-paced and complex world of healthcare, effective communication is vital. Medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, often rely on shorthand and abbreviations to convey information quickly and efficiently. These short forms have become an integral part of their daily practice, enabling them to document patient information, prescribe medications, and communicate with colleagues in a concise manner.
This article aims to explore the list of commonly used short forms in medical settings and shed light on their significance in facilitating smooth communication within the hospital environment. By understanding these abbreviations, both healthcare professionals and patients can enhance their understanding of medical documentation and discussions.”From A to Z: The Essential Short Forms Every Medical Student Should Know” and help you with some content points. Medical doctors and nurses often use a variety of abbreviations and acronyms in their communication.
The List of Short Forms Used by Medical Doctors and Nurses in the Hospital
Decoding the Medical Jargon: A Comprehensive List of Short Forms Used by Medical Doctors and Nurses
Commonly Used Short Forms in Medical Practice
Here are some commonly used abbreviations and acronyms in the medical and nursing fields:
1. MD: Medical Doctor
2. DO: Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine
3. RN: Registered Nurse
4. LPN: Licensed Practical Nurse
5. NP: Nurse Practitioner
6. CNA: Certified Nursing Assistant
7. ICU: Intensive Care Unit
8. ER: Emergency Room
9. OR: Operating Room
10. PT: Physical Therapist
11. OT: Occupational Therapist
12. CT: Computed Tomography
13. MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
14. EKG/ECG: Electrocardiogram
15. CBC: Complete Blood Count
16. IV: Intravenous
17. NPO: Nothing by Mouth
18. PRN: As Needed
19. Rx: Prescription
20. COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Lost in Translation: Unraveling the Abbreviations and Acronyms Used by Medical Professionals
Abbreviations for Medical Conditions and Diseases
1. BP: Blood Pressure
2. HR: Heart Rate
3. RR: Respiratory Rate
4. SpO2: Oxygen Saturation
5. BMI: Body Mass Index
6. Dx: Diagnosis
7. Rx: Treatment/Prescription
8. Hx: Medical History
9. Tx: Treatment
10. H&P: History and Physical Examination
11. ASA: Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin)
12. ICU: Intensive Care Unit
13. PPE: Personal Protective Equipment
14. PRBC: Packed Red Blood Cells
15. EHR: Electronic Health Record
16. DNR: Do Not Resuscitate
17. NKA: No Known Allergies
18. DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis
19. ABG: Arterial Blood Gas
20. PPE: Personal Protective Equipment
Unlocking the Code: Understanding the Common Abbreviations Used in Medical Practice
Examples and explanations
1. CVA: Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke)
2. MI: Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
3. CHF: Congestive Heart Failure
4. COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
5. PUD: Peptic Ulcer Disease
6. UTI: Urinary Tract Infection
7. CAD: Coronary Artery Disease
8. EKG: Electrocardiogram
9. EEG: Electroencephalogram
10. TIA: Transient Ischemic Attack
11. ACLS: Advanced Cardiac Life Support
12. BLS: Basic Life Support
13. MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
14. CT: Computed Tomography
15. PET: Positron Emission Tomography
16. ETOH: Alcohol
17. ROM: Range of Motion
18. DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis
19. NPO: Nothing by Mouth
20. NGT: Nasogastric Tube
21. GI: Gastrointestinal
22. GU: Genitourinary
23. HOB: Head of Bed
24. STAT: Immediately/Urgently
25. PO: By Mouth
26. IV: Intravenous
27. IM: Intramuscular
28. SC: Subcutaneous
29. WBC: White Blood Cell Count
30. RBC: Red Blood Cell Count
31. Hb: Hemoglobin
32. Hct: Hematocrit
33. BUN: Blood Urea Nitrogen
34. CMP: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel
35. ABG: Arterial Blood Gas
36. Fx: Fracture
37. Sx: Symptoms
38. Dx: Diagnosis
39. Rx: Prescription
40. PRN: As Needed
41. H&P: History and Physical Examination
42. C&S: Culture and Sensitivity
43. VRE: Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
44. MRSA: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
45. HSV: Herpes Simplex Virus
46. HPV: Human Papillomavirus
47. HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
48. BPH: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
49. PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
50. PPE: Personal Protective Equipment
Cracking the Medical Language: Exploring the Short Forms Employed by Doctors and Nurses in Hospitals
Abbreviations for Medical Procedures and Tests
1. ARDS: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
2. SIRS: Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome
3. SLE: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
4. RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis
5. IBS: Irritable Bowel Syndrome
6. GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
7. PEEP: Positive End-Expiratory Pressure
8. CPAP: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
9. ABX: Antibiotics
10. C-section: Cesarean Section
11. OB/GYN: Obstetrics and Gynecology
12. PPD: Purified Protein Derivative (Tuberculosis Test)
13. CBC: Complete Blood Count
14. BMP: Basic Metabolic Panel
15. I&D: Incision and Drainage
16. L&D: Labor and Delivery
17. PICC: Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
18. TPN: Total Parenteral Nutrition
19. ESRD: End-Stage Renal Disease
20. LFT: Liver Function Test
21. HRT: Hormone Replacement Therapy
22. FHR: Fetal Heart Rate
23. D&C: Dilatation and Curettage
24. PRBC: Packed Red Blood Cells
25. PPI: Proton Pump Inhibitor
26. TSH: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
27. PT/INR: Prothrombin Time/International Normalized Ratio
28. CVP: Central Venous Pressure
29. SIRS: Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome
30. PEEP: Positive End-Expiratory Pressure
31. CTX: Chemotherapy
32. TPN: Total Parenteral Nutrition
33. HDL: High-Density Lipoprotein
34. LDL: Low-Density Lipoprotein
35. TIBC: Total Iron-Binding Capacity
36. BPH: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
37. CNS: Central Nervous System
38. PNS: Peripheral Nervous System
39. CVA: Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke)
40. DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
41. PTCA: Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
42. CABG: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
43. RSV: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
44. HSV: Herpes Simplex Virus
45. PSA: Prostate-Specific Antigen
46. HAV: Hepatitis A Virus
47. HBV: Hepatitis B Virus
48. HCV: Hepatitis C Virus
49. TURP: Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
50. PSA: Prostate-Specific Antigen
Abbreviations for Medical Specialties and Departments
1. DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
2. GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
3. RRT: Rapid Response Team
4. PFT: Pulmonary Function Test
5. CABG: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
6. BPD: Borderline Personality Disorder
7. GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale
8. VAD: Ventricular Assist Device
9. GSW: Gunshot Wound
10. PPE: Personal Protective Equipment
11. NSTEMI: Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction
12. OTC: Over-the-counter
13. LOC: Level of Consciousness
14. DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis
15. TPA: Tissue Plasminogen Activator
16. ARF: Acute Renal Failure
17. ARDS: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
18. HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
19. AIDS: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
20. ASCVD: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
21. BPH: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
22. BID: Twice a Day
23. TID: Three Times a Day
24. QID: Four Times a Day
25. PO: By Mouth
26. IV: Intravenous
27. IM: Intramuscular
28. SC/SQ: Subcutaneous
29. NPO: Nothing by Mouth
30. PRN: As Needed
31. ADL: Activities of Daily Living
32. H&P: History and Physical Examination
33. CRP: C-reactive Protein
34. HbA1c: Glycated Hemoglobin
35. ABG: Arterial Blood Gas
36. ROM: Range of Motion
37. CTA: Computed Tomography Angiography
38. DRE: Digital Rectal Examination
39. TURP: Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
40. PTT: Partial Thromboplastin Time
41. FFP: Fresh Frozen Plasma
42. CPAP: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
43. PSA: Prostate-Specific Antigen
44. CAUTI: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection
45. DNR: Do Not Resuscitate
46. VRE: Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
47. MRSA: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
48. CRRT: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
49. BSA: Body Surface Area
50. ED: Emergency Department
Abbreviations for Medical Documentation and Charting
1. IBS: Irritable Bowel Syndrome
2. COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
3. HRT: Hormone Replacement Therapy
4. EEG: Electroencephalogram
5. ECG: Electrocardiogram
6. HbA1c: Glycated Hemoglobin
7. CT: Computed Tomography
8. PET: Positron Emission Tomography
9. HCV: Hepatitis C Virus
10. CBT: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
11. NSAID: Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug
12. SIDS: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
13. OCD: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
14. ADHD: Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
15. PTSD: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
16. SLE: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
17. ACL: Anterior Cruciate Ligament
18. HPV: Human Papillomavirus
19. PMS: Premenstrual Syndrome
20. IUD: Intrauterine Device
21. IVP: Intravenous Pyelogram
22. CABG: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
23. TENS: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
24. CBT: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
25. PPE: Personal Protective Equipment
26. HRT: Hormone Replacement Therapy
27. TIA: Transient Ischemic Attack
28. PPI: Proton Pump Inhibitor
29. BPH: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
30. ICP: Intracranial Pressure
31. TBI: Traumatic Brain Injury
32. PEEP: Positive End-Expiratory Pressure
33. SSRI: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor
34. ESR: Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
35. ALT: Alanine Aminotransferase
36. AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase
37. GGT: Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase
38. BMP: Basic Metabolic Panel
39. TSH: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
40. UTI: Urinary Tract Infection
41. ESRD: End-Stage Renal Disease
42. CVA: Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke)
43. NSTEMI: Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction
44. GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
45. PUD: Peptic Ulcer Disease
46. IBD: Inflammatory Bowel Disease
47. CABG: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
48. CRP: C-reactive Protein
49. LMP: Last Menstrual Period
50. NGT: Nasogastric Tube
Streamlining Communication: A Closer Look at the Short Forms Utilized by Medical Professionals in Healthcare Settings
1. IVP: Intravenous Pyelogram
2. BUN: Blood Urea Nitrogen
3. LFT: Liver Function Test
4. CXR: Chest X-ray
5. ICP: Intracranial Pressure
6. FHR: Fetal Heart Rate
7. BPD: Borderline Personality Disorder
8. DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis
9. OCD: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
10. CPAP: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
11. MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
12. ERCP: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
13. IBS: Irritable Bowel Syndrome
14. POTS: Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
15. OCD: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
16. GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
17. RSV: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
18. EEG: Electroencephalogram
19. PEEP: Positive End-Expiratory Pressure
20. TENS: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
21. UTI: Urinary Tract Infection
22. ASD: Atrial Septal Defect
23. HIDA: Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid
24. TURP: Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
25. AML: Acute Myeloid Leukemia
26. IUD: Intrauterine Device
27. PTT: Partial Thromboplastin Time
28. PPD: Purified Protein Derivative
29. H&P: History and Physical Examination
30. PICC: Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
31. EKG: Electrocardiogram
32. FBS: Fasting Blood Sugar
33. PFT: Pulmonary Function Test
34. RSV: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
35. PT/INR: Prothrombin Time/International Normalized Ratio
36. VRE: Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
37. MRSA: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
38. CRRT: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
39. L&D: Labor and Delivery
40. RBC: Red Blood Cell Count
41. WBC: White Blood Cell Count
42. C&S: Culture and Sensitivity
43. BKA: Below-Knee Amputation
44. AED: Automated External Defibrillator
45. IBS: Irritable Bowel Syndrome
46. PCP: Primary Care Physician
47. RSV: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
48. CBC: Complete Blood Count
49. CXR: Chest X-ray
50. CSF: Cerebrospinal Fluid
Navigating the Alphabet Soup: An In-Depth Guide to Short Forms Used by Medical Doctors and Nurses
1. AED: Automated External Defibrillator
2. AV: Atrioventricular
3. BPM: Beats Per Minute
4. C-section: Cesarean Section
5. CT: Computed Tomography
6. DNR: Do Not Resuscitate
7. ENT: Ear, Nose, and Throat
8. Fx: Fracture
9. GFR: Glomerular Filtration Rate
10. H&P: History and Physical Examination
11. HCG: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
12. HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
13. IBD: Inflammatory Bowel Disease
14. ICP: Intracranial Pressure
15. JVD: Jugular Venous Distention
16. LP: Lumbar Puncture
17. MAC: Monitored Anesthesia Care
18. NGT: Nasogastric Tube
19. OR: Operating Room
20. PE: Pulmonary Embolism
21. PICC: Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
22. PPD: Purified Protein Derivative (Tuberculosis Test)
23. PT: Physical Therapy
24. PTT: Partial Thromboplastin Time
25. PVC: Premature Ventricular Contraction
26. RBC: Red Blood Cell Count
27. ROS: Review of Systems
28. SBP: Systolic Blood Pressure
29. SLE: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
30. TPN: Total Parenteral Nutrition
31. UA: Urinalysis
32. VRE: Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus
33. WBC: White Blood Cell Count
34. ABG: Arterial Blood Gas
35. ASA: Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin)
36. BMI: Body Mass Index
37. BPH: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
38. CPT: Current Procedural Terminology
39. CSF: Cerebrospinal Fluid
40. DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
41. DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis
42. ECG/EKG: Electrocardiogram
43. ESRD: End-Stage Renal Disease
44. FHR: Fetal Heart Rate
45. GERD: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
46. GYN: Gynecology
47. HAV: Hepatitis A Virus
48. HBV: Hepatitis B Virus
49. HCV: Hepatitis C Virus
50. HRT: Hormone Replacement Therapy
Shortcut to Clarity: Demystifying the Abbreviations Used in Medical Communication
51. ICU: Intensive Care Unit
52. IUD: Intrauterine Device
53. IVF: In Vitro Fertilization
54. LMP: Last Menstrual Period
55. MI: Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
56. MS: Multiple Sclerosis
57. NPO: Nothing by Mouth
58. OTC: Over-the-counter
59. PACU: Post-Anesthesia Care Unit
60. PET: Positron Emission Tomography
61. PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
62. PMS: Premenstrual Syndrome
63. PTSD: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
64. PUD: Peptic Ulcer Disease
65. ROM: Range of Motion
66. RT: Respiratory Therapist
67. SIDS: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
68. TBI: Traumatic Brain Injury
69. TIA: Transient Ischemic Attack
70. TSH: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
71. UTI: Urinary Tract Infection
72. VSD: Ventricular Septal Defect
73. CVA: Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke)
74. COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
75. CABG: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
76. CPR: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
77. CRRT: Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
78. CPT: Chest Physiotherapy
79. DEXA: Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
80. ESR: Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
81. GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale
82. HCV: Hepatitis C Virus
83. ICD: Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator
84. LVEF: Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction
85. MRCP: Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
86. NSTEMI: Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction
87. OCD: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
88. PAC: Premature Atrial Contraction
89. PALS: Pediatric Advanced Life Support
90. PEG: Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
91. PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
92. PTCA: Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
93. RAST: Radioallergosorbent Test
94. RDS: Respiratory Distress Syndrome
95. SIADH: Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone
96. SLE: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
97. TENS: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
98. TIBC: Total Iron Binding Capacity
99. TURP: Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
100. VSD: Ventricular Septal Defect
Conclusion:
In the fast-paced and demanding field of healthcare, the use of short forms and abbreviations by medical doctors and nurses has become a necessity. These shorthand terms enable efficient and effective communication, allowing healthcare professionals to quickly convey information, document patient records, and coordinate care.
Throughout this article, we have explored the list of commonly used short forms in medical settings and shed light on their significance in facilitating smooth communication within the hospital environment. By understanding these abbreviations, both healthcare professionals and patients can enhance their understanding of medical documentation and discussions.
It is important to recap the importance of short forms in medical practice. They serve as valuable tools for saving time and streamlining communication, enabling healthcare professionals to provide timely and accurate care. However, it is equally crucial to emphasize the need for clear communication and accurate documentation. Misinterpretation or confusion arising from improperly used or misunderstood short forms can have serious consequences for patient safety.
To ensure effective communication, healthcare professionals should prioritize the use of standardized practices, clarify abbreviations when necessary, and strive for context-driven usage. Verification techniques, such as double-checking unfamiliar abbreviations and seeking clarification when in doubt, can also help in promoting accurate communication.
Ultimately, clear communication and accurate documentation are the cornerstones of quality healthcare delivery. By striking a balance between efficiency and clarity, healthcare professionals can maintain accurate records, minimize errors, and provide optimal care to their patients.
In conclusion, short forms play a crucial role in medical practice, allowing for efficient communication in a fast-paced environment. However, it is vital to prioritize clear communication and accurate documentation to ensure patient safety and optimal healthcare outcomes.
For more information, resources, and guidelines on medical abbreviations and communication, healthcare professionals can visit reputable sources and consult with their organizations or professional associations.
Remember, in the world of healthcare, effective communication saves lives.
Custom Message: For more information and resources related to healthcare and optimal health, visit optimalhealth.in.
Always ensure accurate and clear communication when using these abbreviations and acronyms in medical and nursing settings. Use these abbreviations and acronyms accurately and within the appropriate context to ensure effective communication in medical and nursing settings.
Remember to use these abbreviations and acronyms accurately and within the appropriate context to ensure effective communication in medical and nursing settings.
Please note that it’s important to use these abbreviations and acronyms appropriately and ensure clear communication within the medical and nursing fields.
Nursing Career 101: The A to Z FAQ Guide
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
1. Are short forms used internationally or do they vary by region?
Short forms used by medical doctors and nurses can vary to some extent by region or country. While there are many commonly recognized abbreviations and acronyms that are used internationally, there may also be regional or institutional variations.
2. How can healthcare professionals ensure that short forms are understood by all members of the healthcare team?
To ensure that short forms are understood by all members of the healthcare team, healthcare professionals can take the following measures: 1. Use standardized abbreviations, 2. Provide context, 3. Document abbreviations in patient records, 4. Effective communication, 5. Ongoing education and training, and 6. Encourage open dialogue.
3. Are there any instances where the use of short forms is discouraged?
1. Patient communication, 2. High-stakes situations, 3. Error-prone abbreviations, 4. Legal and regulatory considerations, and 5. Cross-cultural communication.
4. What resources are available to healthcare professionals for learning and understanding medical abbreviations?
Healthcare professionals have access to a variety of resources to learn and understand medical abbreviations. Some of these resources include:
1. Medical dictionaries and glossaries, 2. Professional organization guidelines, 3. Medical textbooks and reference books, 4. Online databases and websites, 5. Continuing education courses, and 6. Hospital or institutional resources.
5. How can patients ensure they understand the short forms used in their medical records?
1. Ask for clarification, 2. Request a patient-friendly explanation, 3. Utilize educational resources, 4. Keep a personal health record, 5. Engage in open communication, 6. Seek a second opinion, if needed